Overview
Most on-network scanners (ARP-SCAN, NMAP, NSLOOKUP, DIG) rely on scanning specific network interfaces and subnets. Check the subnets documentation for help on this setting, especially VLANs, what VLANs are supported, or how to figure out the network mask and your interface.
An alternative to on-network scanners is to enable some other Device scanners/importers that don't rely on NetAlertX having access to the network (UNIFI, dhcp.leases, PiHole, etc.).
Note: The scan time itself depends on the number of IP addresses to check so set this up carefully with the appropriate network mask and interface.
Note
If you have a lot of offline devices, which should be online, look into using, or substituing, ARP scan with other scans, such as
NMAPDEV. The ARP scan protocol uses a cache so results may not be 100% reliable. You can find all available network scanning options (marked as🔍 dev scanner) in the Plugins overview readme.
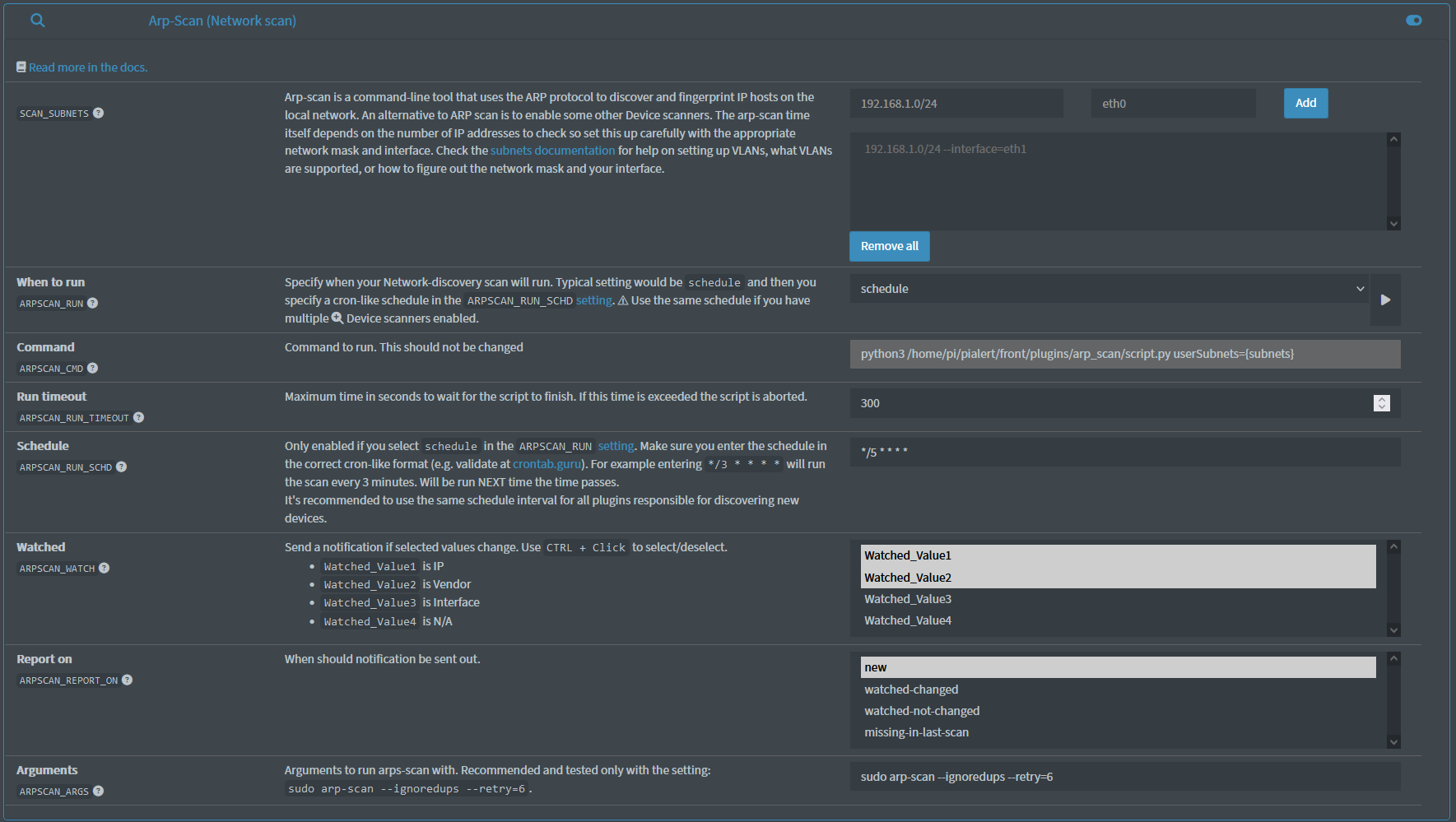
Usage
- Go to settings and set the
SCAN_SUBNETSsetting as per subnets documentation. - Enable the plugin by changing the RUN parameter from disabled to your preferred run time (usually:
schedule).- Specify the schedule in the
ARPSCAN_RUN_SCHDsetting
- Specify the schedule in the
- Adjust the timeout if needed in the
ARPSCAN_RUN_TIMEOUTsetting - Review remaining settings
- SAVE
- Wait for the next scan to finish
Common issues
IP flipping on Google Nest devices
Some devices might flip IP addresses after each scan triggering false notifications. This is because some devices respond to broadcast calls and thus different IPs after scans are logged. To preven this you can try to use the --exclude-broadcast flag in the ARPSCAN_ARGS setting or change the SCAN_SUBNETS setting from e.g.: 192.168.1.0/24 to 192.168.1.1-192.168.1.254 to exclude the broadcast address 192.168.1.255 from the scanned range.
Examples
Settings: